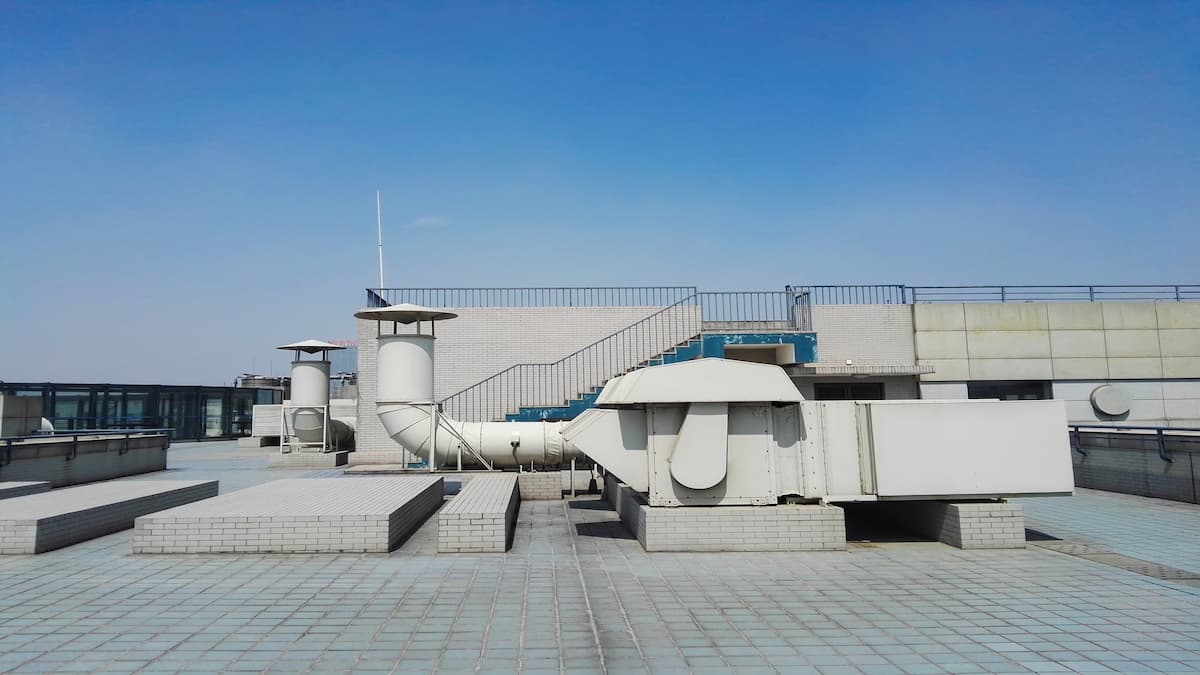
How Chilling Plants Work: A Beginner’s Guide to Industrial Cooling
Chilling plants play a crucial role in industrial cooling by maintaining optimal temperatures for machinery and processes. These systems use advanced cooling systems like air cooled chillers and water-cooled chiller units to manage heat effectively. This guide explains how a chiller system works and its importance in modern industries.
What Is a Chilling Plant?
A chilling plant is a machine used to remove heat from a process or space. It uses a refrigeration cycle to cool water or other fluids. This chilled water is then circulated to maintain the temperature of industrial equipment or spaces. Chilling plants are not the same as household HVAC systems. While HVAC systems cool air in residential or commercial spaces, industrial chillers are designed for large-scale processes and machinery. They are more powerful and are built for continuous operation.
In industrial cooling applications, chilling plants are key to maintaining precise temperatures. They support critical processes by ensuring temperature stability, reducing downtime, and improving product quality.
Where Are Chilling Plants Used?
Chilling plants are used in many industries where precise temperature control systems are required.
Food & Beverage Industry:
Used for food industry cooling during processing, packaging, and storage. Chilling plants help preserve freshness, ensure food safety, and meet hygiene standards by maintaining strict temperature control systems across all stages.
Plastic & Injection Molding:
Essential for mold temperature control and reducing cycle times. Chilling plants increase production efficiency, improve product consistency, and prevent defects by keeping mold temperatures stable using chilled water systems.
Chemical Processing:
Maintain specific reaction temperatures and improve safety. Accurate temperature control systems prevent overheating, reduce hazardous reactions, and enhance product quality, making industrial chillers vital in chemical plants and production environments.
Data Centers & Pharma:
Ensure constant cooling for equipment and sensitive environments. Chilling plants help avoid overheating, protect sensitive components, and ensure regulatory compliance by delivering uninterrupted industrial cooling to critical infrastructure and storage areas.
Key Components of a Chilling Plant
Compressor – Heart of the System
The compressor compresses refrigerant gas and moves it through the system. It is the main driver of the refrigeration cycle.
Evaporator & Condenser – Heat Transfer Basics
The evaporator absorbs heat from the process water, while the condenser releases heat into the environment. These are vital in managing heat exchange.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve regulates refrigerant flow into the evaporator, helping control the temperature and pressure.
Cooling Tower vs Air-Cooled Units
A cooling tower is used in water cooled chiller systems to remove heat. In contrast, air cooled chillers use ambient air to cool the refrigerant. Both serve different setups based on space, climate, and cooling needs.
How a Chilling Plant Works (Simplified Refrigeration Cycle)
The refrigeration cycle in a chilling plant follows these steps:
Compressor: Compressor compresses low-pressure gas into high-pressure gas. The compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas, enabling it to flow through the system efficiently and begin the refrigeration cycle for effective industrial cooling.
Condenser: The condenser cools and converts gas to liquid. In the condenser, high-pressure refrigerant gas releases heat and changes into a liquid. This step is critical for removing heat from the system via air cooled or water cooled chillers.
Expansion Valve: The expansion valve reduces the pressure of the refrigerant. The expansion valve allows the high-pressure liquid refrigerant to expand, lowering its pressure and temperature before entering the evaporator. This prepares the refrigerant to absorb heat during the next phase.
Evaporator: In the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat and turns back to gas. The evaporator is where the chilled refrigerant takes in heat from the chilled water system. This causes it to evaporate, cooling the surrounding process or equipment in industrial chilling plants.
The cycle repeats: Once the refrigerant turns back into gas, it returns to the compressor, and the refrigeration cycle starts over. This continuous loop ensures precise and reliable temperature control systems for various industries.
This process removes heat from the water or fluid, creating a reliable temperature control system for industrial use.
Types of Chilling Plants
Air-Cooled Chillers
Air cooled chillers use ambient air to remove heat. They are easier to install and maintain. Best for outdoor use and smaller operations.
Water-Cooled Chillers
Water cooled chillers use water and a cooling tower to reduce heat. They are more efficient in large setups but need more maintenance.
Ammonia Chillers
Use ammonia as the refrigerant. Common in industries with high cooling demands. Lower operational costs but require safety measures.
Pros & Cons:
- Air cooled chillers: Easy setup, less efficient.
- Water cooled chiller: More efficient, complex setup.
- Ammonia chillers: Cost-effective, safety concerns.
Temperature Control & Chilled Water Systems
Chilling plants use a chilled water system to circulate cold water through a loop. The chilled water loop keeps the temperature stable across equipment or processes.
The temperature control system adjusts the flow and cooling based on the required output. Common process water temperatures range from 6°C to 15°C, depending on the industry.
Maintenance Basics for Chilling Plants
Regular maintenance ensures performance and long life. A chiller maintenance checklist includes:
- Weekly visual checks
- Monthly cleaning of filters and coils
- Monitoring refrigerant and water levels
Maintaining correct chiller capacity helps improve energy efficiency and reduce costs.
Choosing the Right Chilling Plant Manufacturer
Selecting the right chilling plant manufacturer ensures efficient performance, system reliability, and long-term support for your industrial cooling requirements.
Experience in industrial chillers: Choose a manufacturer with years of experience in designing and delivering industrial chillers. Proven industry knowledge ensures better system design, improved reliability, and support tailored to your specific industrial cooling and temperature control system needs.
Proven energy efficiency: Look for chilling plant manufacturers that prioritize energy-efficient systems. Efficient cooling systems reduce electricity consumption, lower operating costs, and contribute to sustainable operations—especially important in high-demand environments like manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and data center applications.
Ability to customize systems: Every facility has unique cooling needs. A reliable manufacturer should offer flexible solutions, from air cooled chillers to water cooled chillers, tailored to your process requirements, space constraints, and desired chiller capacity for optimal performance.
Check for certifications, good technical support, and reliable after-sales service: Choose a vendor with industry certifications, skilled technical teams, and prompt after-sales service. This ensures compliance, long-term system efficiency, and quick resolution of issues in your chilled water system or overall chiller system.
Need Help Choosing a Chilling System?
Choosing the right chiller system can improve efficiency and product quality. For reliable chilling plants, Contact Refcon Chillers. We offer customized industrial cooling solutions with top-tier service and support.
Get in touch with Refcon Chillers for expert advice and custom solutions. Let’s find the perfect industrial cooling system for your application!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between a chiller and a cooling tower?
A chiller cools fluid directly, while a cooling tower removes heat from the water cooled chiller system.
How much does a chilling plant cost to run?
Costs vary based on chiller capacity, energy efficiency, system type, and operational hours within your temperature control system.
Which industries need chilling plants the most?
Industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and data centers rely on chilling plants for precise industrial cooling.